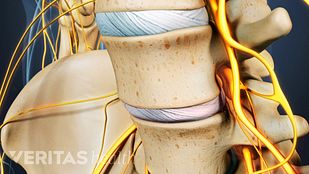
Some of the terms used when trying to diagnose neck or back pain can be confusing. Making matters even more complicated, medical professionals may use different terms to refer to the same condition.
Here are some commonly confused terms to know when discussing neck or back pain.
椎间盘退变性疾病与骨关节炎
椎间盘退变性疾病和骨关节炎是两个脊柱的最常见的退化性疾病。雷竞技下载网址
- 椎间盘退变性疾病实际上不是一种疾病,而是一种退行性过程。由于椎间盘的年龄,他们自然会失去一些水分和高度随着时间的推移。眼泪可以在光盘的保护外层的发展,可能导致疼痛。
- Facet joint osteoarthritisoccurs when the protective cartilage within one or more facet joints wears down between the vertebrae. The joint becomes swollen and arthritic as osteophytes (bone spurs) grow, enlarging the joint and causing more inflammation and potentially pain.
椎间盘退变性疾病and osteoarthritis typically occur simultaneously in the spine, because when either a disc or nearby facet joint starts to breakdown, it puts more pressure on the other. This process becomes recurrent and increases the likelihood of further degeneration of both these structures. Even when both of these conditions are present, medical professionals may refer to the problem differently depending on preferred terminology or which is causing the most problematic symptoms.
阅读更多:Facet Joint Disorders and Back Pain
病是用于脊柱变性和其相关的症状,其也常用于描述小关节的骨关节炎和/或退变性椎间盘疾病的涵盖性术语。
SeeSpondylosis: What It Actually Means
椎间盘突出vs. Bulging Disc
椎间盘突出是颈部和背部疼痛的常见来源,但它并不总是相同的,为椎间盘膨出。
- Bulging discoccurs when the disc’s protective outer layer (annulus fibrosus) bulges out beyond the vertebral body or normal disc space. In a bulging disc, the jelly-like inner portion (nucleus pulposus) does not leak into the outer layer.
- Herniated discoccurs when the disc’s nucleus pulposus starts to leak into cracks or tears in the outer layer. There are different stages of a herniated disc:
- 椎间盘突出occurs when the nucleus pulposus leaks into the outer layer but not beyond its boundary.
- 椎间盘脱出当髓核开始泄漏外层的边界之外发生。
- 光盘封存当光盘的一个部分或片段从盘的其余部分分离发生。
The terms ruptured disc or slipped disc may be used to refer to a herniated disc. It is important to note that even when a disc is herniated, it stays strongly attached to the adjacent vertebrae and does not actually slip.
阅读更多:What's a Herniated Disc, Pinched Nerve, Bulging Disc...?
In This Article:
神经根病vs. Radicular Pain
这是经常听到医生和病人都可以互换使用的术语神经根病和根性疼痛。但是,技术上的差异。
- Radicular painoccurs when a nerve root becomes inflamed and radiates pain from the spine, such as to an arm or leg. Radicular pain can range from mild to sharp or electric-like, but it does not involve neurological deficits.
- 神经根病occurs when nerve root inflammation or damage causes a change in neurological function, which can be measured and verified. For example, cervical radiculopathy may involve numbness and/or weakness that goes into the arm or hand. If a neurological deficit cannot be verified, such as with electrodiagnostic testing, radiculopathy cannot be diagnosed.
While radiculopathy typically includes radicular pain, it is not a requirement.
阅读更多:神经根,神经根炎和根性疼痛
症状vs. Signs
许多医生病人ref的简化语言erring just to symptoms when meaning both symptoms and signs.
- 症状refer to the evidence of illness or injury that a person experiences or feels, but cannot prove or demonstrate for a doctor. A few examples include pain, tingling, fatigue, or nausea.
- 迹象指的是可以与测试或观察来验证疾病或伤害的证据。一些实例包括虚弱,骨折,发热,或呕吐。
A case of chronic neck or back pain may be particularly hard to diagnose if there are only symptoms present without verifiable signs to help further narrow down what might be wrong.
When to Ask for Clarification
If a doctor or other medical professional uses an unfamiliar term or says something confusing when explaining a diagnosis, it is important to ask for clarification. Fully understanding the diagnosis can help a patient make better decisions about the treatment options.